If you’re familiar with Photoshop, you know that blend modes are one of the most useful tools available in image editing. With over 27 blend modes to choose from, there are endless possibilities for creating unique visual effects. Despite the extensive range of blend modes offered within the program, it can still be a challenge to accurately predict outcomes.
When playing with blend modes, it is always helpful to familiarize yourself with the descriptions and keyboard shortcuts associated with each blend mode beforehand in order to get the best results. If used correctly, blend modes provide vast creative and technical flexibility to help users enhance their artwork.
Blending mode groups and descriptions
First, let’s see how to separate blend modes in separate groups. We can save time by knowing the possible result.

Normal
This is the default mode and there is no visible effect applied.
Dissolve
Random replacement of the pixel depending on the opacity. Photoshop takes those pixels and displays them, randomly. In a similar way to a speckled effect
Darken
Compares the color information for each pixel and replaces pixels lighter than the blend color. Pixels darker than the blend color are not affected.
Multiply
Multiplies pixels of the top layer with the corresponding pixels of the bottom layer. The result is always a darker picture. Also, Multiplying any color with black produces black. Multiply blend mode is very commonly used.
Color Burn
This blend mode darkens the top layer by increasing the contrast. Blending with white produces no visible effect.
Linear Burn
Similar to color burn but instead of increasing contrast, linear burn decreases the brightness to darken the base color. Also, blending with white color produces no change.
Darker Color
Darker Color picks the darker colors between upper and lower layers.
Lighten
Pixels in the base layer that are darker than the blend color are replaced. Pixels that are lighter are left unchanged.
Screen
Multiplies the inverse of the blend and base colors. The result is always a lighter color. Using screen mode with black leaves the color unchanged.
Color Dodge
Brightens the base color and decreases the contrast between the two layers. Blending with black color produces no change. Commonly used and work great for light effects.
Linear Dodge (Add)
Linear Dodge is the opposite of Linear Burn. Increases brightness to lighten the base color. It is also similar to the Screen blend mode but with a more intense result.
Lighter Color
Lighter Color compares and selects the lighter base or blend color. Pixels darker than the blend color are replaced.
[adinserter block=”2″]
Overlay
Overlay combines multiply and screen blend modes depending on the base color. light becomes lighter and dark become darker.
Soft Light
Depending on the blend color if is lighter than 50% gray, the image is lightened. If the blend color is darker than 50% gray, the image is darkened. Similar to dodging and burning.
Hard Light
Hard Light blend mode combines multiply and screen modes. Useful for adding highlights and shadows.
Vivid Light
Combines color dodge and color burn blend modes. Dodge applies when blend color is lighter than 50% gray and burn if the blend color is darker than 50% gray.
Linear Light
Combines linear dodge and linear burn blend modes. Dodge applies if the blend color is lighter than 50% gray. The image is lightened by increasing the brightness. Burn applies to darker values.
Pin Light
Pin Light replaces colors depending on the brightness of the blend color. Pin Light is primarily used for creating special effects to an image.
Hard Mix
The result of hard mix blend mode is either 0 or 255 for each channel. Changes all pixels to primary additive colors.
Difference
The difference highlights the differences between the blend layer and the base layer. Blending with black color produces no change.
Exclusion
Similar to difference blend mode but the contrast is lower. Blending with black color produces no change.
Subtract
Subtracts the blend color from the base color.
Divide
Divides the blend color from the base color.
Hue
Hue applies the hue of the blend color to the base image. Retains the luminance and saturation of the base image.
Saturation
Saturation applies the saturation of the blend color to the base image. Retains the hue and luminance of the base image.
Color
Color blend mode takes the grey levels of the base color and colors them with the blend color.
Luminosity
Luminosity applies the luminosity of the blend colors to the base image. Retains the hue and saturation of the base image.
Blending mode examples
These examples show the result of each blend mode in Photoshop.
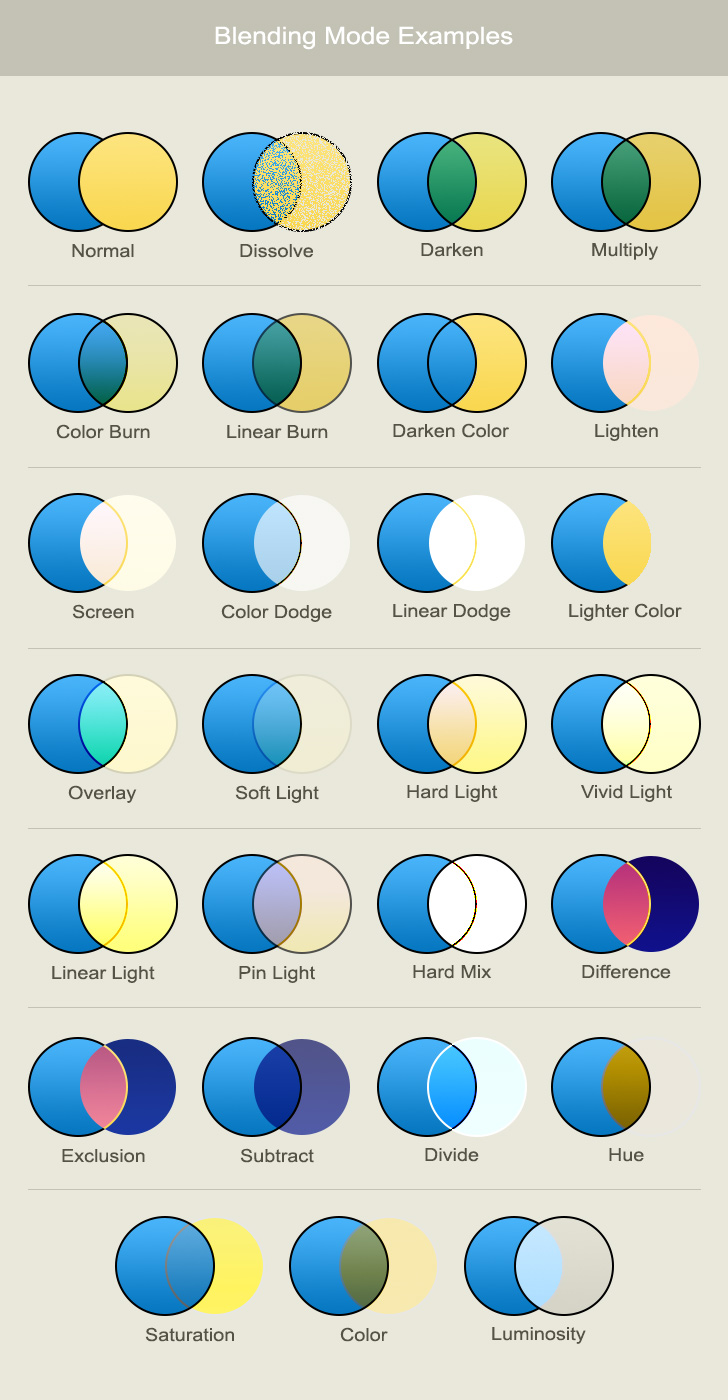
Commonly used blending modes
The most commonly used blend modes in Photoshop. Multiply for darkening, screen and color dodge for lightening. For contrast, overlay and soft light blend modes.

Blending mode keyboard shortcuts
To save time from your projects use the keyboard shortcuts in this list.

15,000+
Design Assets
- Instant Access
- Free Content Updates
- Constantly Growing Library
- Unlimited Downloads
- Simple Licensing


By Dreamstale
Get creative with our free & premium design resources. Download a vast collection of graphic design materials, such as graphics, sublimation designs, icons, textures, stock photos and more.
Plus get access to Photoshop tutorials & inspirational articles that will spark your imagination.